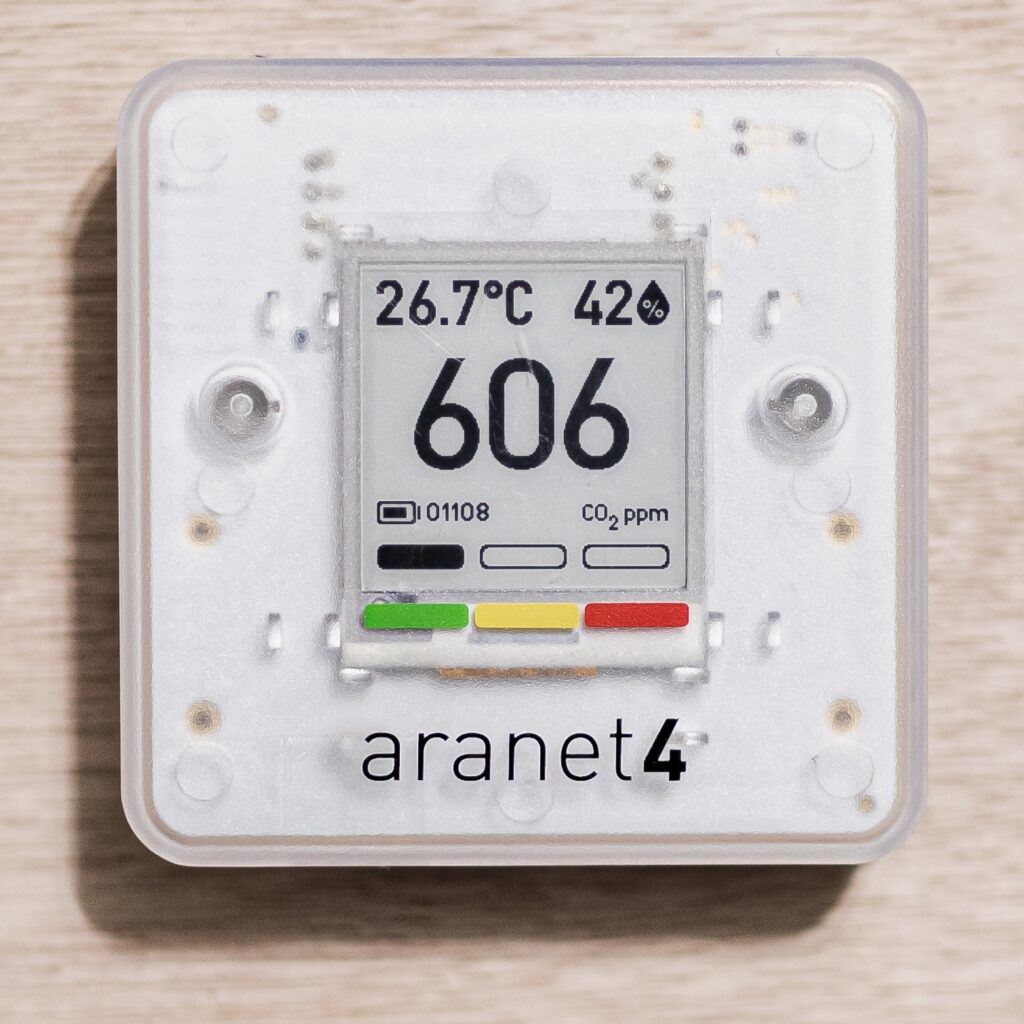
Overview
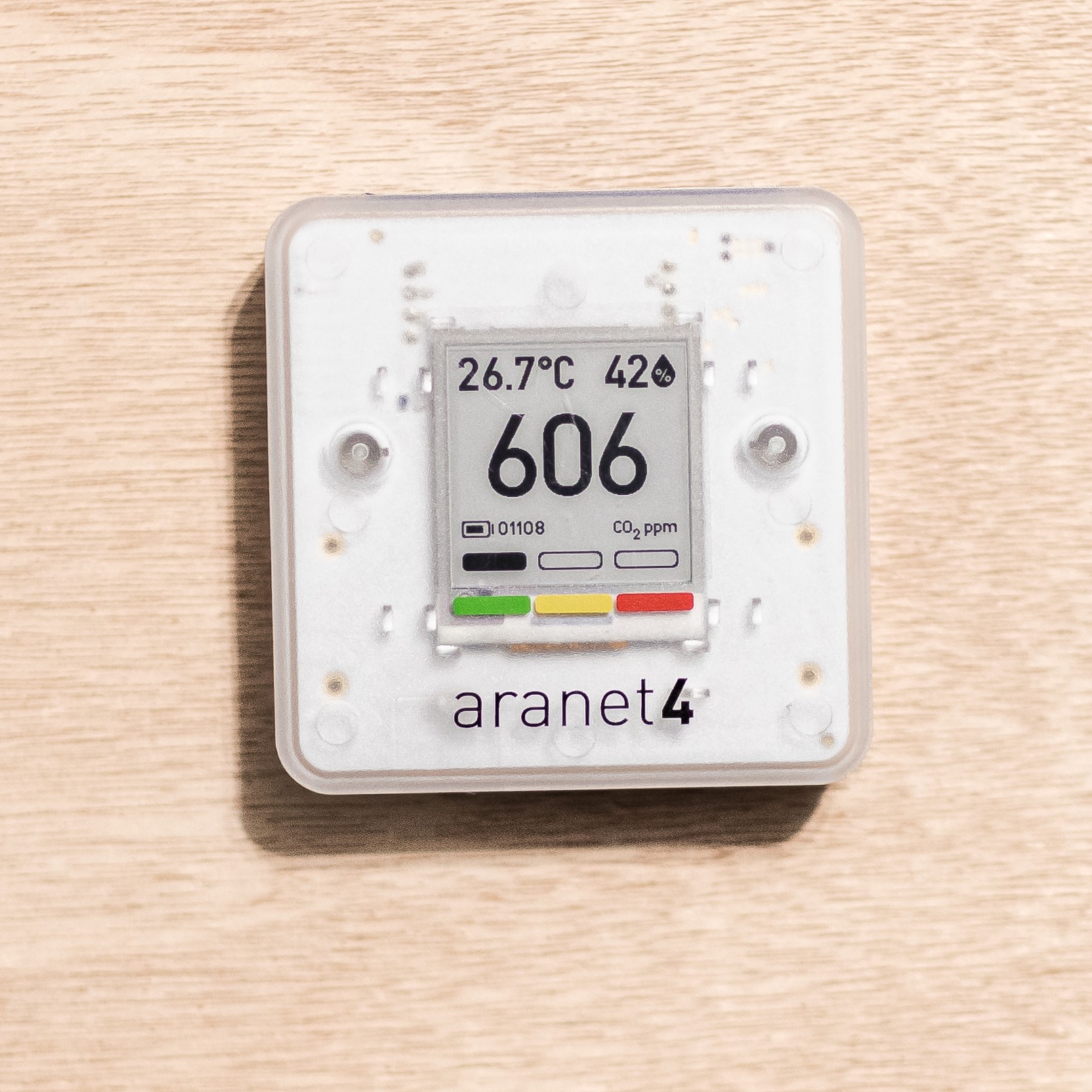
Ventilation is one of the main environmental controls to minimize the transmission of airborne viruses, including SARS-CoV-2 indoors. By using carbon dioxide sensors to estimate ventilation, religious communities can evaluate the safety of conducting indoor services, as well as understand the density of people (occupancy) within houses of worship.
The program was designed to assist populations that have been disproportionately impacted by COVID-19, and to empower those communities to gather and support their community in a safe, healthy space when possible under CDC guidance.
Indoor Air Quality & Places of Worship
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of well-ventilated spaces, which can significantly reduce the likelihood of contracting COVID-19. Some states allow for in-person worship, and there are significant concerns:
- Gatherings of people in unventilated indoor spaces where airborne viruses can accumulate increases the odds of SARS-CoV-2 transmission. The virus can accumulate up to an order of magnitude faster when the congregation is singing or speaking during the service.
- Adults aged 65 and older are more likely to attend religious services, an age group particularly vulnerable to hospitalization or death due to COVID-19.
- Churches and older buildings may have inadequate or outdated ventilation systems.
Outreach
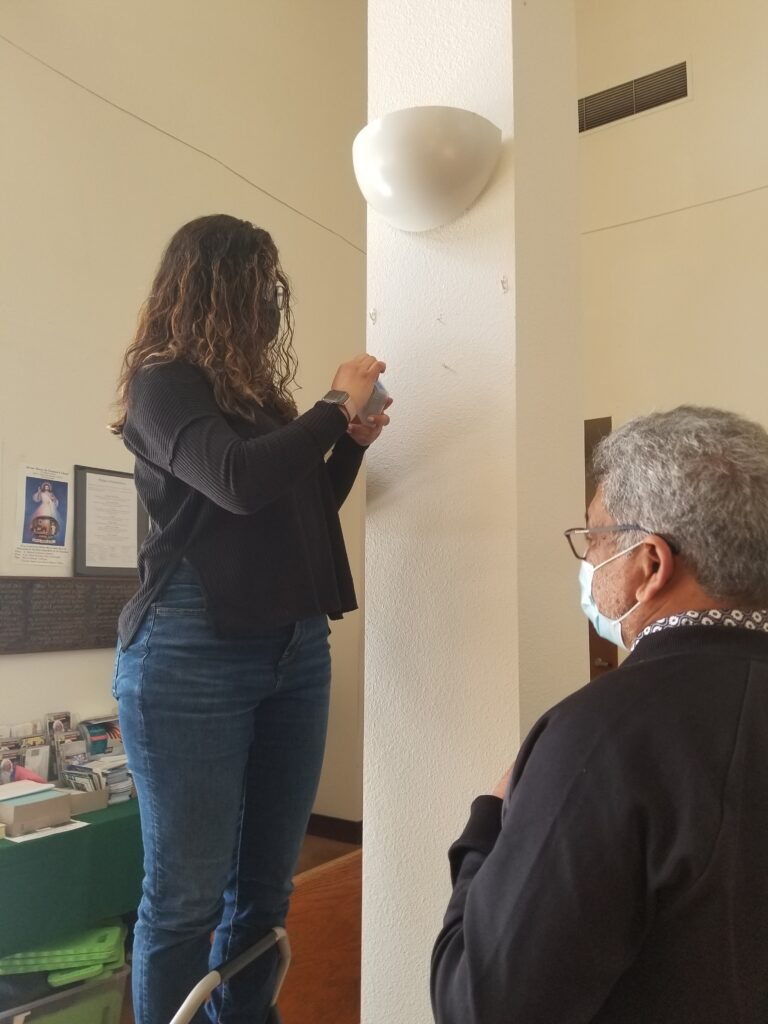
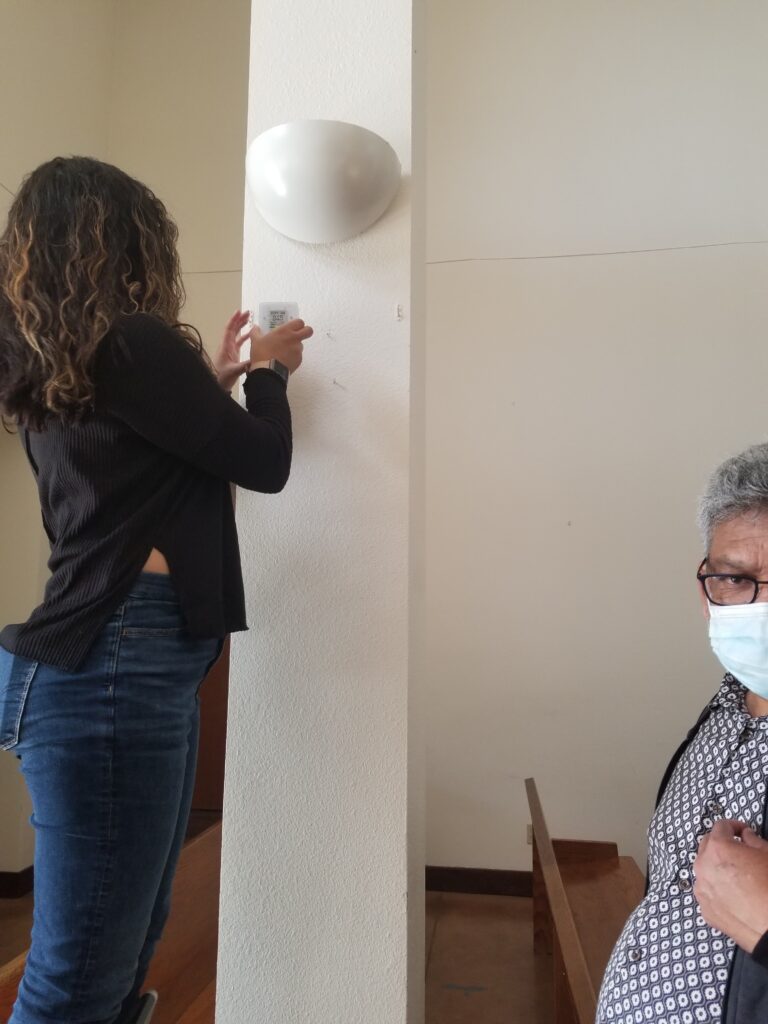
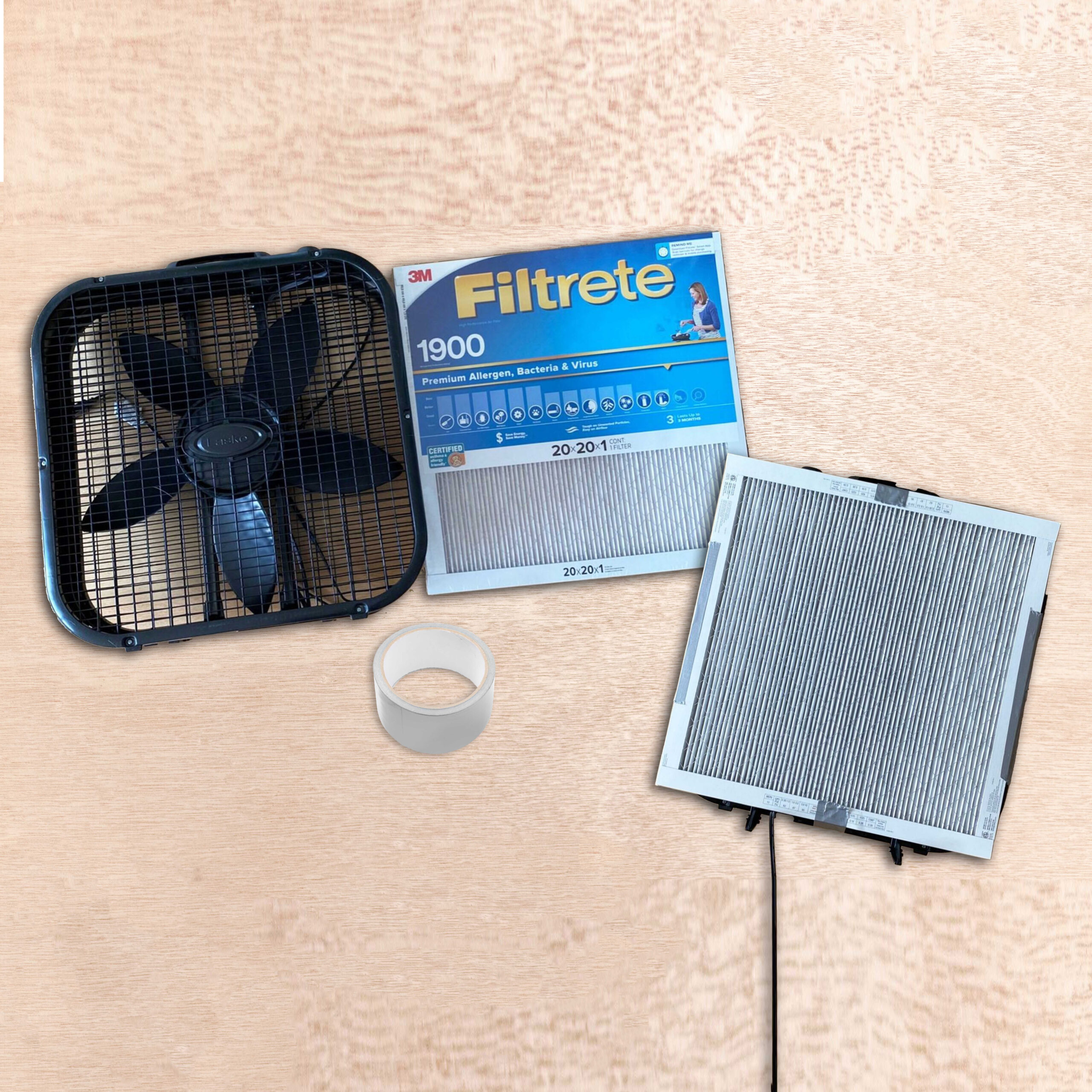
With our partners, we were able to provide helpful information on how to calibrate the equipment, where to best position their sensors for accurate data collection, and how to interpret the data. Afterwards, we provided information on how to improve ventilation within their space.